A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Treating, and Living with Bursitis
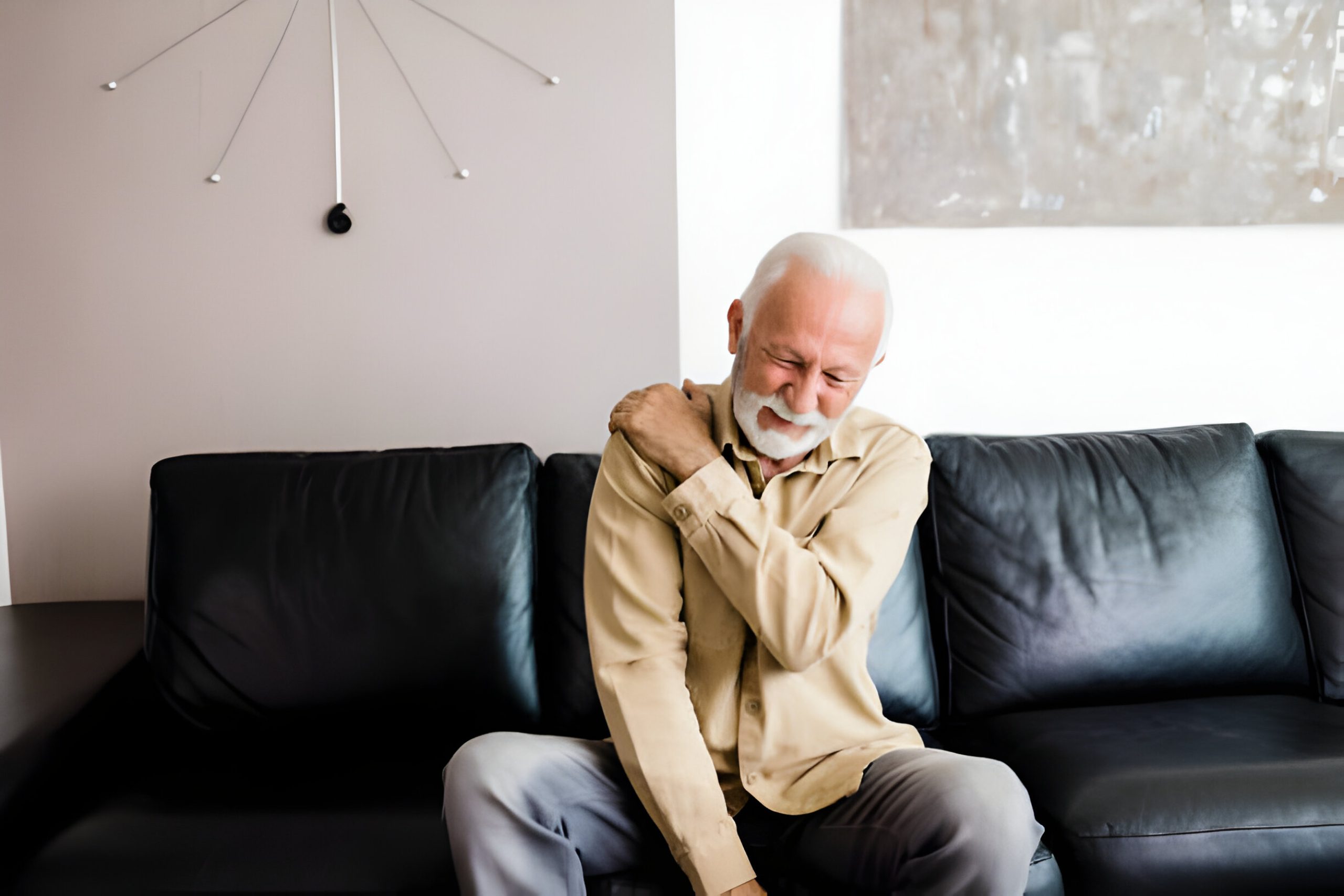
Bursitis, a common condition characterized by painful swelling in the bursae—small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles—can disrupt your daily life. This condition often affects the shoulders, elbows, knees, and hips, and while it can be painful and limiting, understanding its nature, treatment options, and how to manage it can help you achieve relief and return to your normal activities. In this article, we’ll explore whether bursitis can fully heal, providing an in-depth look at its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, management, and prevention. We’ll also highlight the specialized care available at Veda Medical Plastic Surgery to support your recovery.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa, a small, fluid-filled sac located between bones and soft tissues such as muscles and tendons. Bursae function like cushioning pads, reducing friction and allowing smooth movement between structures. When a bursa becomes irritated, it swells, leading to discomfort, pain, and restricted movement. Bursitis can develop suddenly or gradually, often in response to repetitive stress or trauma.
Types of Bursitis
With over 150 bursae in the human body, bursitis can affect any of them. The most common types include:
- Shoulders: Subacromial bursitis occurs in the shoulder and is often associated with rotator cuff injuries.
- Elbows: Olecranon bursitis, sometimes called miner’s elbow, affects the elbow’s bursa and is common in activities that involve repetitive elbow use.
- Knees: Prepatellar bursitis, also known as housemaid’s knee, affects the bursa in front of the kneecap and is often due to prolonged kneeling.
- Feet: Bursitis near the heel (calcaneal bursitis) or big toe (metatarsal bursitis) can be caused by improper footwear or excessive pressure.
- Hips: Trochanteric bursitis affects the outer side of the hip and is often associated with activities that involve repeated hip movements.
- Buttocks: Ischial bursitis, or weaver’s bottom, affects the bursa located near the sitting bones and is common in people who sit for prolonged periods.
Symptoms and Causes
What are Bursitis Symptoms?
The primary symptoms of bursitis include:
- Pain: Often sharp and exacerbated by movement or pressure on the affected area.
- Swelling: Noticeable around the joint or bursa.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the affected joint fully.
In cases where bursitis is caused by an infection, additional symptoms might include:
- Redness: Discoloration on the skin over the affected bursa.
- Warmth: A feeling of warmth in the inflamed area.
- Fever and Chills: Systemic symptoms that indicate a possible infection.
What Causes Bursitis?
Bursitis can result from various factors, including:
- Repetitive Motions: Activities that involve repeated stress on a joint, such as sports (e.g., throwing a baseball) or manual labor (e.g., lifting heavy boxes).
- Prolonged Pressure: Actions that put continuous pressure on a joint, such as kneeling or leaning on elbows.
- Injuries: Trauma to the area can lead to bursitis.
- Infections: Bacterial infections can cause bursitis, particularly if there is a break in the skin near the bursa.
Risk Factors for Bursitis
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing bursitis:
- Athletes: Sports involving repetitive movements can stress the bursae.
- Manual Laborers: Physical work often involves repetitive motions or heavy lifting.
- Musicians: Instrument playing can lead to bursitis due to repetitive hand or arm movements.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid disease can increase susceptibility to bursitis.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is Bursitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of bursitis typically begins with a physical examination. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms, medical history, and any activities that may have contributed to the condition.
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm a diagnosis of bursitis and rule out other conditions, your provider may recommend:
- X-rays: To exclude other causes of joint pain, such as fractures or bone spurs.
- Ultrasound or MRI: Imaging techniques that can reveal inflammation or swelling in the bursa.
- Blood Tests: To identify signs of infection or other underlying conditions.
- Fluid Aspiration: A procedure where fluid is drawn from the bursa to check for infection or other issues.
Management and Treatment
Best Ways to Treat Bursitis
Treatment for bursitis focuses on relieving pain and reducing inflammation:
- Rest: Avoid activities that exacerbate the condition to give the bursa time to heal.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce swelling and pain.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area elevated to minimize swelling.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
Additional Treatment Options
If conservative treatments are insufficient, your healthcare provider may suggest:
- Antibiotics: For bursitis caused by bacterial infections.
- Physical Therapy: To restore mobility and strength in the affected joint.
- Occupational Therapy: To learn new techniques or modifications to prevent stress on the bursa.
- Corticosteroid Injections: To reduce severe inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: In rare cases where bursitis persists despite other treatments, surgical removal of the bursa may be necessary.
Prevention
How to Prevent Bursitis
Preventing bursitis involves reducing the risk factors associated with the condition:
- Proper Technique: Use correct posture and techniques in sports and work activities to avoid unnecessary stress on joints.
- Gradual Introduction: Ease into new exercises or activities to prevent injury.
- Avoid Prolonged Pressure: Take breaks from positions that put excessive pressure on your joints, such as kneeling or sitting for long periods.
- Use Cushions and Pads: Protect vulnerable areas with appropriate padding.
Outlook / Prognosis
Duration of Bursitis
Most cases of bursitis resolve within a few weeks with appropriate treatment. However, returning to activities too soon can risk reinjury.
Impact on Work or School
If your work or activities contributed to bursitis, you may need to take time off or modify your routine during recovery. Discuss necessary adjustments with your healthcare provider.
Chronic Bursitis
Repeated episodes of bursitis can lead to a chronic condition. Chronic bursitis may cause long-term issues with joint mobility and increased susceptibility to future flare-ups.
Living With Bursitis
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent Pain: Pain that interferes with daily activities and does not improve with home treatment.
- Recurrence: Bursitis that returns after treatment.
- Systemic Symptoms: Signs of infection, such as fever or significant redness and warmth in the affected area.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- What type of bursitis do I have?
- Are any diagnostic tests necessary?
- What treatment options are available, and how long will recovery take?
- When can I safely resume my normal activities?
Additional Common Questions
What is the Difference Between Bursitis and Arthritis?
While both conditions affect the joints, bursitis is usually caused by inflammation of the bursa and is often temporary. Arthritis, on the other hand, involves long-term degeneration of the joint’s cartilage and requires ongoing management.
What is the Difference Between Bursitis and Tendinitis?
Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursae, while tendinitis affects the tendons connecting muscles to bones. Both conditions share similarities in their causes and treatments but involve different tissues.
Veda Medical Plastic Surgery: Your Partner in Recovery
At Veda Medical Plastic Surgery in San Antonio, TX, we offer expert care to help you manage and recover from bursitis. Founded in 2006 by Dr. Pradeep S. Mohan, our clinic provides state-of-the-art treatments and personalized care. Alongside Dr. Mohan, our team includes Andrew Vidal APRN, MSN, FNP-C, WOC-RN, and Yolanda Sodair, M.A., all dedicated to supporting your health and recovery.
Our comprehensive approach ensures that you receive the highest quality care, whether you need medical treatment or cosmetic services. Our modern facility is equipped with the latest technologies to support your healing process and provide effective, affordable solutions tailored to your needs.
Contact Us for a Consultation
Phone: 210-566-8332 / 210-361-6617
Location: 12315 Judson Rd., Live Oak, TX 78233
Email: office@vedamedical.com
Open Hours
Mon – Fri: 8:00am to 5:00pm
Sun: Closed
Every 2nd and 4th Sunday: 10:00am – 4:00pm
At Veda Medical, we are committed to making a positive difference in your life by offering expert care and support for your recovery. Reach out to us today to start your journey towards healing and improved well-being.